
|
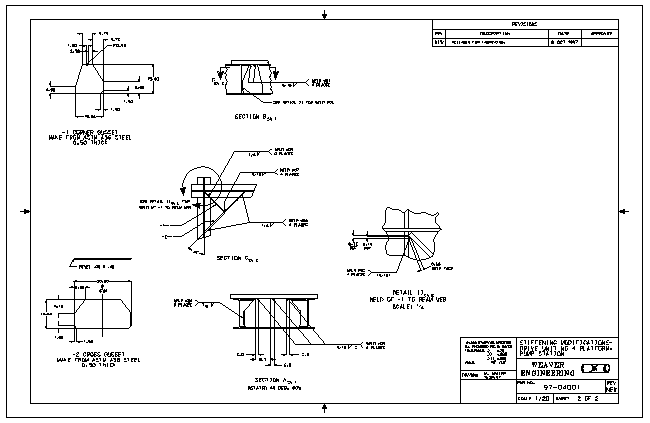
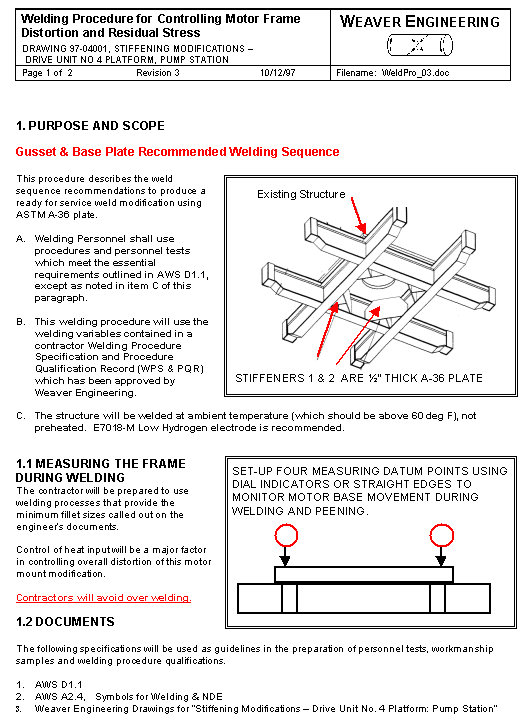
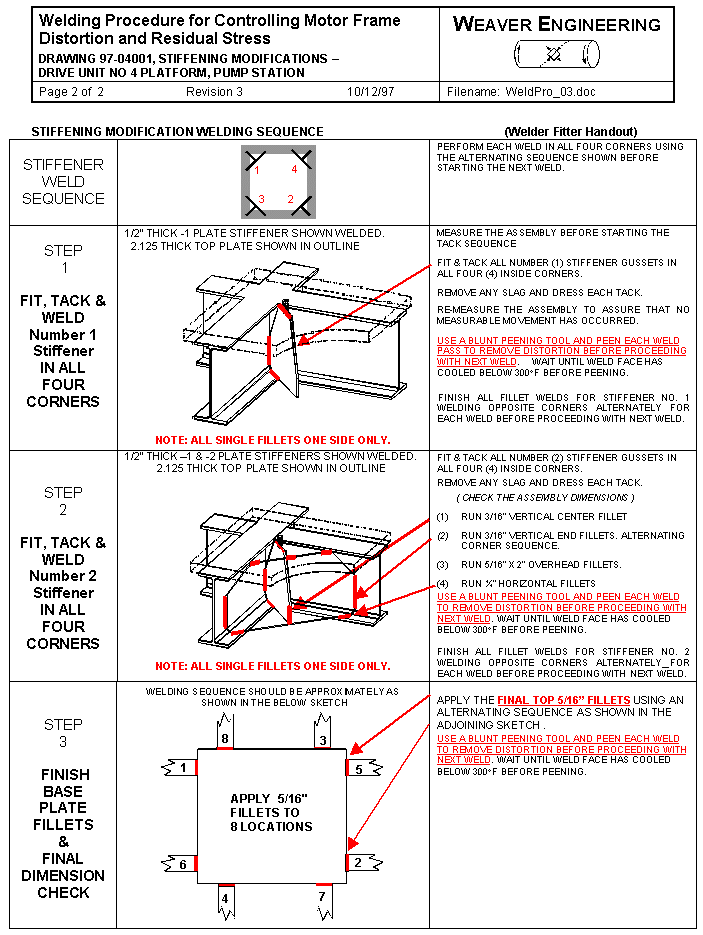
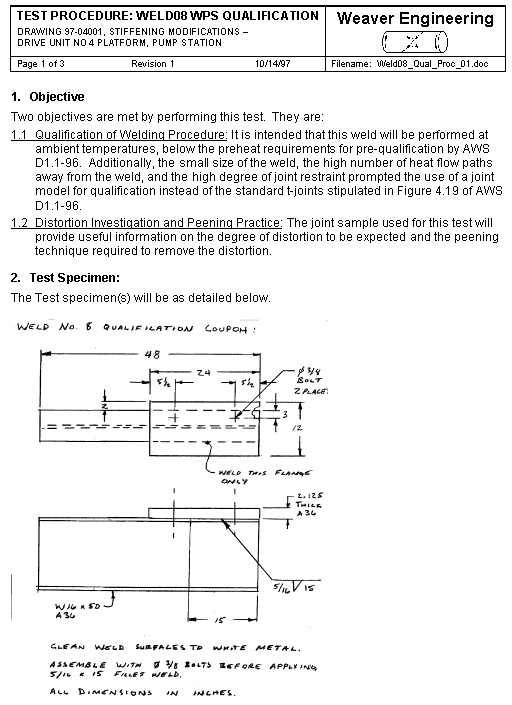
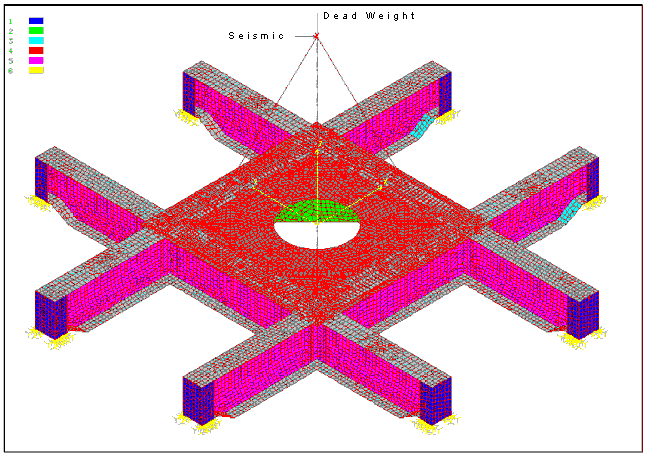
Above is a platform for an 18,000 pound motor and clutch assembly, the shaft is vertical. The clutch will be a new modification to the existing system. The addition of the clutch, by itís mass addition and because it raises the c.g. of the motor, would lower the resonate frequency of the existing structure to within the operating range of the motor. The objective of the engineering undertaken was to increase the stiffness of the platform to raise the resonate frequency out of the operating range of the motor. The parallelism of the motor mounting surface to the frame supports is important. These surfaces were machined parallel after stress relief on the original weldment. The addition of stiffeners with minimal welding distortion and residual stress was a design objective. Of benefit is the fact that the original frame was designed for stiffness and the service stresses are very low. Presented are the resulting design, analysis for weld requirements, distortion control procedure for welding, and a weld qualification test procedure where preheat was to be avoided. The final configuration achieved the stiffness objective with minimal welding and distortion less than 0.0005 inch. |
|
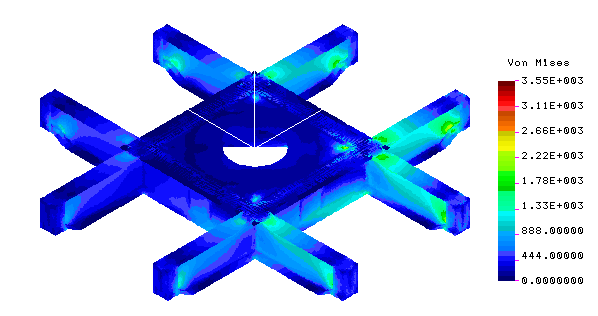
Finite element analysis (FEA) was used to evaluate the stiffness improvements for a variety of configurations evaluated. FEA was also used to evaluate stresses in the existing structure, stresses in the modifications and, in conjunction with FEWeld, determine the weld throat requirements for the modifications. |
 |
|
|
|